728x90
크루스칼(Kruskal) 알고리즘
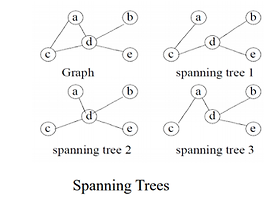
- 간선의 가중치 정보를 이용해 MST(최소신장트리)를 구현하는 알고리즘 이다.
- 이용되는 알고리즘은 Union Find, 우선순위 큐가 있다.
1) 전체 로직 순서
- Comparable을 상속받아 Edge 클래스(정점1, 정점2, 가중치)를 선언한다.
- compareTo를 오버라이딩 하여 가중치를 기준으로 오름차순 정렬을 조건을 추가한다.
- Edge형 우선순위큐를 선언하고 주어진 간선의 정보를 이용해 새로운 edge 객체를 우선순위큐에 넣어준다.
- 우선순위큐에서 간선을 순서대로 빼온다.
- 빼온 간선에 해당하는 두 정점이 같은 Union인지 확인한다.
- 같은 Union이라면 -> 이미 추가된 정점들이므로 다음 간선을 빼낸다
- 다른 Union이라면 -> 해당 정점의 부모노드를 이용해 같은 Union으로 결합시킨다, 가중치는 결과값에 누적시킨다.
- MST가 완성될때 까지 (4,5,6,7)과정을 반복한다.
- union시킨 횟수+1이 정점의 갯수와 같아진다면 break!! (모든 정점이 간선으로 연결되었다는 뜻)
2) 실제 구현 코드
문제: sw expert (최소스패닝트리) 참고
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class swea최소스패닝트리_크루스칼버전 {
static class Edge implements Comparable<Edge>{
int from;
int to;
int weight;
Edge(int from, int to, int weight){
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge o) { //간선기준 오름차순 정렬을 위해
return this.weight-o.weight;
}
}
static int nodenum ;
static int edgenum ;
static int[] v_parent;
static void makeset() { //unionfind 초기화
for(int i=1; i<=nodenum; i++) {
v_parent[i]=i;
}
}
static void unionset(int node1, int node2) { // union 결합
int node1p = findset(node1);
int node2p = findset(node2);
if(node1p>node2p)v_parent[node2p]=node1p;
else v_parent[node1p]=node2p;
}
static int findset(int nodenum) { //union 대장 찾기
if(v_parent[nodenum]==nodenum)return nodenum;
else return v_parent[nodenum] = findset(v_parent[nodenum]);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int tc = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine()); //tc입력
for(int t=1; t<=tc; t++) {
StringTokenizer ST = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
nodenum = Integer.parseInt(ST.nextToken());
edgenum = Integer.parseInt(ST.nextToken());
PriorityQueue<Edge> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(); //간선정보 넣을 pq
for(int k=0; k<edgenum; k++) {
ST = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int from = Integer.parseInt(ST.nextToken());
int to = Integer.parseInt(ST.nextToken());
int weight = Integer.parseInt(ST.nextToken());
pq.add(new Edge(from,to,weight)); //우선순위큐에 간선정보넣기
}
v_parent = new int[nodenum+1]; //node번호 1부터니까 +1로 선언
makeset(); //자기 자신으로 부모 셋팅
long result = 0;
int setnum = 1;
for(int i=0; i<edgenum; i++) { //pq에서 하나씩 꺼내면서 union만들기
Edge now = pq.poll();
int nowfrom = now.from;
int nowto = now.to;
int nowweight = now.weight;
if(findset(nowfrom)==findset(nowto))continue; //같은 유니온일때
else {
unionset(nowfrom, nowto);
result+=nowweight; //누적 가중치
setnum++;
//System.out.println("from:"+nowfrom+" to:"+nowto+" weight:"+nowweight);
}
//System.out.println(Arrays.toString(v_parent));
if(setnum==nodenum)break;
}
System.out.println("#"+t+" "+result);
}
}
}
3) 시간 복잡도
'자료구조, 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [알고리즘] 최소신장트리, MST란? (0) | 2022.03.30 |
|---|---|
| 우선순위 큐는 왜 힙 구조를 사용할까? (0) | 2022.03.01 |
| 힙(Heap)의 구조와 동작과정 (0) | 2022.03.01 |
| 트리(Tree)의 개념과 종류들 (0) | 2022.03.01 |
| 스택(Stack)과 큐(Queue) (0) | 2022.03.01 |